Goaltide Daily Current Affairs 2020
Current Affair 1:
Coloured cotton from India on the cusp of commercial release in 2021
India has been the home to naturally occurring coloured cotton. The research and commercial release of these varieties had been hampered in the past due to the fear of these varieties contaminating the white cotton.
With the Government of India and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research paying attention to coloured cotton research in the recent years, there could be a commercial release in 2021. The promise of release of naturally-coloured cotton from India could help reduce the environmental pollution caused by dyes. As colour dyes pollute more water bodies and damage the environment, the search for fabric that is naturally coloured and can be grown organically (as cotton uses a lot of pesticides) has gained momentum.

Similar developments in other countries:
Recently, an important breakthrough was achieved in Australia, and its two billion-dollar cotton industry is anxiously awaiting new research by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) scientists. The plant breeders here have genetically modified cotton to create coloured cotton in black and other rich, dark colours which could become a “game changer” in the years to come.
Since the 1980s, California-based Sally Fox, has made brown cotton famous the world over. China is already a leader in coloured cotton. However, of late the slave-factory style of production using Uighurs, has come under global censure.
Similar development can be seen in India too:

Shades of brown more stable
Among coloured cotton genotypes, shades of brown are more stable than green genotypes which tend to fade when exposed to the sun.
Ok, now we will learn something more about Cotton in India.
Cotton is one of the most important cash crops and accounts for around 25% of the total global fibre production.







Current Affair 2:
Crime in India report for 2019- Part 2
Part 1 we have covered yesterday. This article will purely help in mentioning examples of law and order, rape cases, under reporting, etc. So, read once.
In an earlier story, we looked at the numbers pertaining to cognizable and violent crimes registered in 2019 across different states.
In this story, we look at the incidence of certain violent crimes such as murder which cannot be hidden and may have near 100% reporting and compare it with the crime rate of offences against women such as rape and assault all of which may not be reported to the police. The comparison might help get a better understanding of the variance in crime rates among states and if there is any under-reporting in some states.
One in four of the registered violent crime in 2019 is a kidnapping
Around 1.05 lakh cases were booked as kidnapping and abduction in 2019, under IPC sections 363-369 and constitute over a quarter of the violent crimes.

In more than 94% of the rape cases, the offender was known to the victim
A total of 12 States/UTs had a higher violent crime rate than the national rate. Delhi, Odisha, West Bengal, Haryana, Bihar, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Jharkhand which together accounted for close to 56% of the registered violent crimes.

Among the violent crimes, murders and dowry deaths are the most probable ones to get reported. On the other hand, the probability of reporting in the case of rape and other crimes against women is comparatively lower because of the social stigma attached to it. Hence, these crimes tend to get under-reported as victims often do not come forward to report it. The NCRB report for 2019 indicates that in case of registered instances of rape, the offender was known to the victim in more than 94% cases meaning that the offender could be a family member, friend or an acquaintance making it more difficult for the victim to report.
Rate of Murder, Dowry deaths & Kidnapping in India
The crime rate for murder across states reveals that Jharkhand had the highest murder rate of 4.3 per lakh population in 2019, almost twice the national rate. Assam, which recorded the highest violent crime rate had a murder rate of 3.6. Assam, which recorded the highest violent crime rate had a murder rate of 3.6. States of Bihar, Delhi, and Madhya Pradesh have also recorded a murder rate above national rate.

UP recorded among the lowest rate of rape cases in 2019
Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan have recorded the highest number of rapes in the country and together constitute more than 28% of the rape cases in India in 2019.
Under cases registered under ‘Assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty’, Delhi and Kerala are among the top five states with high rates of crime under this section whereas Bihar has recorded the least and Uttar Pradesh falls below the national rate.
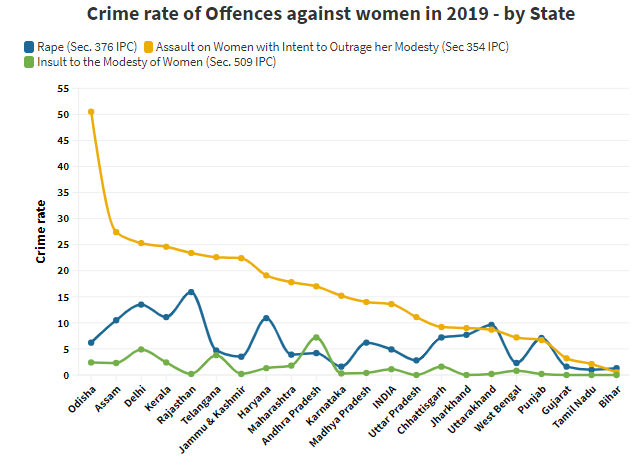
It has to be noted that the most populous states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Maharashtra have a lower overall crime rate. However, the crime rate in the case of murders, dowry deaths, and kidnappings in Uttar Pradesh is higher. Gujarat and Kerala have lower numbers of such crimes and lower rates. For instance, in the case of dowry deaths, UP reported 300 times more dowry deaths in 2019 compared to Kerala.
What this could mean is that in the case of crimes where there is a probability of under-reporting, crime rates in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are on the lower side compared to the higher rates in states like Delhi & Kerala which are more literate.
What is evident is that some states like Kerala and Delhi are doing better than others in reporting and registering crimes, which may be the reason behind the higher overall crime rates.
A study conducted by TISS (Tata Institute of Social Sciences) and sponsored by Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPRD), an organization under the Ministry of Home, titled ‘A Study on Non-Registration of Crimes: Problems & Solutions’ conducted across six states identified the following to be the reasons behind under-reporting.
- Police are burdened with heavy workload and long working hours which prompted them to avoid more work by registering less cases.
- Behaviour of police towards the complainants, mainly women and marginalized sections of society discouraged people from reporting a crime.
- Budget allocation for the police is low which has resulted in shortage of manpower, infrastructure and transport.
- Management of crime statistics by police functionaries has linkages with performance appraisals of police.
- Classification of cognizable and non-cognizable nature of crimes of which a normal citizen is unaware is exploited by police to twist the complaint
- Police may get loaded with false complaints to investigate.
- Interface of political/NGO/Media and other influential person in the process of registration of crime
- Corruption
All of this indicates that a higher or a lower crime rate is not at all an indicator of the functioning of the police and also does not reflect the status of the law & order in a particular state. Reporting & registration of a crime are essential for an efficient criminal justice system and steps must be taken to ensure these.
Current Affair 3:
DRDO successfully tests ASW missile system
News - The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully test-fired the missile-assisted release of a lightweight anti-submarine torpedo System for anti-submarine warfare (ASW), Supersonic Missile Assisted Release of Torpedo (SMART)

- SMART is a missile assisted release of lightweight anti-submarine torpedo system for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) operations far beyond the torpedo range. This launch and demonstration are significant in establishing anti-submarine warfare capabilities.
- All the mission objectives including missile flight up to the range and altitude, release of torpedo and deployment of velocity reduction mechanism have been met perfectly.
- The flight testing of SMART follows the successful test firing on Saturday of its indigenously developed nuclear capable hypersonic missile ‘Shaurya’ with a strike range of around 1,000 km from the test range.
- The test was conducted from APJ Abdul Kalam Island (earlier known as Wheeler Island), off the Odisha coast.
- It covers most of its flight in the air at lower altitudes with two-way data link from the warship or an airborne submarine target detection system and provides the exact location of the hostile submarine to correct its flight path midway
- Just when it approaches close enough to the submerged submarine, the missile will eject the torpedo system into the water and the autonomous torpedo will start moving towards its target to take out the submarine

Current Affair 4:
Tata Group to unveil India’s first CRISPR test: FELUDA (FNCas9 Editor Limited Uniform Detection Assay)

The Tata Group has announced that the Tata CRISPR test developed by CSIR-IGIB, ‘Feluda’ (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology) had received regulatory approvals from the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) for commercial roll- out in accordance with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) guidelines.
In this regard we will understand the CRISPR and then we will talk about FELUDA.
What is CRISPR - Cas9 technology?
CRISPR – Clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeats, is the technology and Cas9 is the protein that acts like a scissor.
- CRISPR technology is basically a gene-editing technology that can be used for the purpose of altering genetic expression or changing the genome of an organism.
- This technique is based on the natural defense mechanism found in some bacteria.
- It uses a specific enzyme — Cas9 — to identify and eliminate predetermined genes and DNA sequences.
- The technology can be used for targeting specific stretches of an entire genetic code or editing the DNA at particular locations.
- Its many potential applications include correcting genetic defects, treating and preventing the spread of diseases and improving crops.
- It is a cheaper, more effective, and endlessly adaptable form of gene manipulation, and it seems to work in every model organism.
How CRISPR - Cas9 technology works?
- In bacteria, Cas9 carries crRNA — the genetic information of viruses to identify where to make their cuts.
- The specific location of the genetic codes that need to be changed, or “edited”, is identified on the DNA strand, and then, using the Cas9 protein, which acts like a pair of scissors, that location is cut off from the strand. A DNA strand, when broken, has a natural tendency to repair itself.
- If Cas9 is assigned a specific RNA sequence and delivered to cells, it will hunt down corresponding sequences in the cellular DNA housed in the nuclei and perform a double-strand cut, severing the entire helix at a predetermined point.
- Scientists intervene during this auto-repair process, supplying the desired sequence of genetic codes that binds itself with the broken DNA strand.

Why is FELUDA (COVID-19 Test) important?
High detection rates:
The test has met high benchmarks, with 96% sensitivity and 98% specificity for detecting the novel coronavirus. The Tata CRISPR test achieves the accuracy levels of the traditional RT-PCR (real- time polymerase chain reaction) tests
More effective (Time and Money)
It has quicker turnaround time, less expensive equipment, and better ease of use.
First Covid-19 test to use CRISPR technology
The Tata CRISPR test is the world’s first diagnostic test to deploy a specially adapted Cas9 protein to successfully detect the virus causing COVID-19.
A step towards indigenization
This marks a significant achievement for the Indian scientific community, moving from R&D to a high-accuracy, scalable and reliable test in less than 100 days. It uses indigenously developed CRISPR technology for the detection of the genomic sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.

<< Previous Next >>



