Goaltide Daily Current Affairs 2020
Current Affair 1:
Building a Greener Recovery: Lessons from the Great Recession- A new UNEP Report
Name of the report is important. We are just giving outline what is mentioned in the report. You don’t need more than this.
The paper, Building a Greener Recovery: Lessons from the Great Recession, is the first in a series of UNEP reports designed to help countries build back more sustainably from the pandemic.
This report presents the impact of the global public health and economic crisis created by the pandemic and the growing financial burden on governments. The lack of adequate international support and coordination for ensuring progress towards the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) has exposed the vulnerability of developing countries to the pandemic.
The report also reviews efforts to introduce green stimulus and recovery efforts during the Great Recession, as well as key trends since then.

It then discusses their implications for constructing a post-pandemic green recovery strategy for both G20 and low and middle-income countries today, and how such a strategy can lead to inclusive green growth.
The persistent underpricing of fossil fuels globally is the most significant deterrent to green structural transformation and innovation.

The paper also suggested differing legislative approaches in developed and developing countries. For low- and middle-income states, many of which are under extreme fiscal pressure because of the pandemic, the report recommended:
- replacing fossil fuel subsidies with investments in clean energy and expanding access to renewable energy in rural areas
- reallocating irrigation subsidies to improve water supply, sanitation and wastewater infrastructure; and
- implementing a “tropical carbon tax” to fund reforestation and ecological restoration. This is a levy on fossil fuels that is invested in natural climate solutions (NCS) aimed at conserving, restoring and improving land management to protect biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Current Affair 2:
World Habitat Day
We have mainly taken this topic to explain you the most important topic- United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat)
The United Nations designated the first Monday of October of every year as World Habitat Day to reflect on the state of our towns and cities, and on the basic right of all to adequate shelter. The Day is also intended to remind the world that we all have the power and the responsibility to shape the future of our cities and towns.

Measures taken by Indian Government to improve life in URBAN:
- Major flagship Missions such as Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban, the Smart Cities Mission, the AMRUT Mission were in implementation mode in India well before the SDGs were adopted by the other Member States.
- Housing: There is a huge focus on the use of new and environmentally safe construction technologies and techniques. Through a global housing technology challenge (GHTC), the very best of national and international technologies are sought to be brought in. GHTC aims to fast-track the construction of affordable housing and meet the target of constructing 1.2 crore houses by 2022.
- Urban Poor: The PM SVANidhi scheme targeting the street vendors who were affected by the lockdown that was imposed. A collateral free working capital of Rs.10,000 is made available to the street vendors immediately by the participating banks.
- National urban policy framework 2018 seeks to rebuild Indian cities around clusters of human capital, instead of considering them simply as an agglomeration of land use.

UN Report on Population says:
The report speculates that by 2050, the urban population will have increased to 87.7 million and the rural population will account for 78.3 million people. However, this overhaul will take place somewhere after 2045 itself, suggests the data.

Now, United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat)
UN-Habitat is the United Nations programme working towards a better urban future. Its mission is to promote socially and environmentally sustainable human settlements development and the achievement of adequate shelter for all. We see its evolution, history. Topic will be clearer to you then.
Read Now.
- On 1 January 1975, the UN General Assembly established the United Nations Habitat and Human Settlements Foundation (UNHHSF), the first official UN body dedicated to urbanization.
- Then under the umbrella of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), its task was to assist national programmes relating to human settlements through the provision of capital and technical assistance, particularly in developing countries.
- At the time, urbanization and its impacts were less prominent in the UN agenda, mainly because two-thirds of humanity was still rural.
- The first international UN conference to fully recognize the challenge of urbanization was held in 1976 in Vancouver, Canada. This conference – Habitat I – resulted in the creation, on 19 December 1977, of the precursors of UN-Habitat: the United Nations Commission on Human Settlements – an intergovernmental body – and the United Nations Centre for Human Settlements (commonly referred to as “Habitat”), which served as the executive secretariat of the Commission.
- In 1996, the United Nations held a second conference on cities – Habitat II – in Istanbul, Turkey to assess two decades of progress since Habitat I in Vancouver and to set fresh goals for the new millennium.
- On 1 January 2002, through General Assembly Resolution, Habitat’s mandate was strengthened, and its status elevated to a fully-fledged programme in the UN system, giving birth to UN-Habitat, the United Nations Human Settlements Programme.
- In 2015, member states approved the Sustainable Development Goals including a dedicated goal for urban development, SDG11 which calls to “Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable.” A year later, at the UN Conference on Housing and Sustainable Urban Development – Habitat III – member states signed the New Urban Agenda. This is an action-oriented document which sets global standards of achieving SDG11, rethinking the way we build, manage, and live in cities.
We will also see World Urban Forum (WUF).
The World Urban Forum (WUF) is the world’s premier conference on urban issues. It was established in 2001 by the United Nations to examine one of the most pressing issues facing the world today: rapid urbanization and its impact on communities, cities, economies, climate change and policies.
Organized and convened by UN-Habitat, the Forum has become one of the most open gatherings on the international arena, for exchanging views and experiences on urban challenges.

World Economic Forum 2020 summit was held in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
Current Affair 3:
THSTI: Part of Vaccine Assessment Project

The Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness for Innovation (CEPI), a global initiative, has named Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad as one of the six laboratories for assessing Covid-19 vaccine candidates that are under development.
The mandate of the bioassay laboratory at the Faridabad-based THSTI, a premier research institute under the DBT, is to provide validated assays for vaccine development at par with global standards. The CEPI network will initially involve six laboratories, one each in Canada, Britain, Italy, the Netherlands, Bangladesh and India. Under the CEPI global network, the laboratories will use the same reagents and follow a common set of protocols to measure the immune response of multiple vaccine candidates under development and trial.


CEPI is an innovative global partnership between public, private, philanthropic, and civil society organizations launched in Davos in 2017 to develop vaccines to stop future epidemics.
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations’ (CEPI’s) mission is to stimulate and accelerate the development of vaccines against emerging infectious diseases and enable access to these vaccines for people during outbreaks.
India-CEPI
The Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science & Technology, and Government of India has been implementing the Ind-CEPI mission ‘India Centric Epidemic Preparedness through Rapid Vaccine Development: Supporting Indian Vaccine Development’.
The objectives of this mission are aligned with that of CEPI and aims to strengthen the development of vaccines and associated competencies/technologies for the diseases of epidemic potential in India.
Current Affair 4:
40% of the Amazon Rainforest Is at Tipping Point to Becoming Savanna


Much of the Amazon could be on the verge of losing its distinct nature and switching from a closed canopy rainforest to an open savannah with far fewer trees due to the chronic stresses of deforestation and climate change.
Why they are saying Savannah?
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. See Savannah biome below:

Now, more about news:
New research shows that this tipping point could be much closer than previously thought.

As much as 40% of the existing Amazon rainforest is now at a point where it could exist as a savannah instead of as rainforest, according to a study published in the journal Nature Communications.

Any shift from rainforest to savannah would still take decades to take full effect, but once under way the process is hard to reverse. Rainforests support a vastly greater range of species than savannah and play a much greater role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Parts of the Amazon are receiving much less rain than they used to because of the changing climate. Rainfall in about 40% of the forest is now at a level where the rainforest could be expected to exist as savannah instead, according to the study, led by the Stockholm Resilience Centre, based on computer models and data analysis.
Current Affair 5:
Kamath Panel Report
Background
The Reserve Bank of India as part of its Statement on Developmental and Regulatory Policies released a ‘Resolution Framework for Covid-19 related Stress’, dated August 6, 2020.
The Resolution Framework inter alia envisages constitution of an Expert Committee (Committee) under the Chairmanship of Shri K V Kamath with following composition:
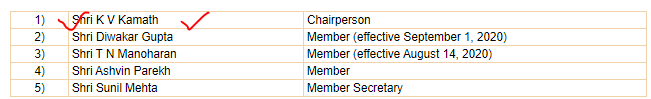
The first and foremost task before the Committee was to identify the sectors where the impact of Covid-19 was visible.
The Committee recognizes that:
- The Covid-19 pandemic has affected the best of companies.
- These businesses were otherwise viable under pre-Covid-19 scenario.
- Impact is pervasive across several sectors but with varying severity – mild, moderate and severe.
Recommendations made by the Committee:
- Graded approach to restructuring of stressed accounts based on severity of the impact on the borrowers- Banks can classify the accounts into mild, moderate and severe as recommended by the committee.
- Five financial parameters to gauge the health of sectors facing difficulties- total outside liabilities to adjusted tangible net worth, total debt to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (Ebitda), debt service coverage ratio (DSCR), current ratio and average debt service coverage ratio (ADSCR).

- 26 sectors have been identified including auto, aviation, construction, hospitality, power, real estate and tourism.
The Supreme Court recently asked the Centre and the Reserve Bank of India about the steps taken to implement the K.V. Kamath Committee report on recommendations to bail out sectors affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Why these measures were necessary? How serious is the debt problem?
- Corporate sector debt worth Rs 15.52 lakh crore has come under stress after Covid-19 hit India, while another Rs 22.20 lakh crore was already under stress before the pandemic.
- This effectively means Rs 37.72 lakh crore (72% of the banking sector debt to industry) remains under stress.
- This is almost 37% of the total non-food bank credit.
- Besides, Companies in sectors such as retail trade, wholesale trade, roads and textiles are facing stress. Sectors that have been under stress pre-Covid include NBFCs, power, steel, real estate and construction.



