Goaltide Daily Current Affairs 2022
Current Affair 1:
Indian Tourism Statistics 2022
I am here covering few important data. Just go through below images. Have a basic idea. No need to remember everything.
Inbound Tourism: Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs), Arrivals of Non-Residents Indians (NRIs) and International Tourist Arrivals (ITAs) 2001-2021
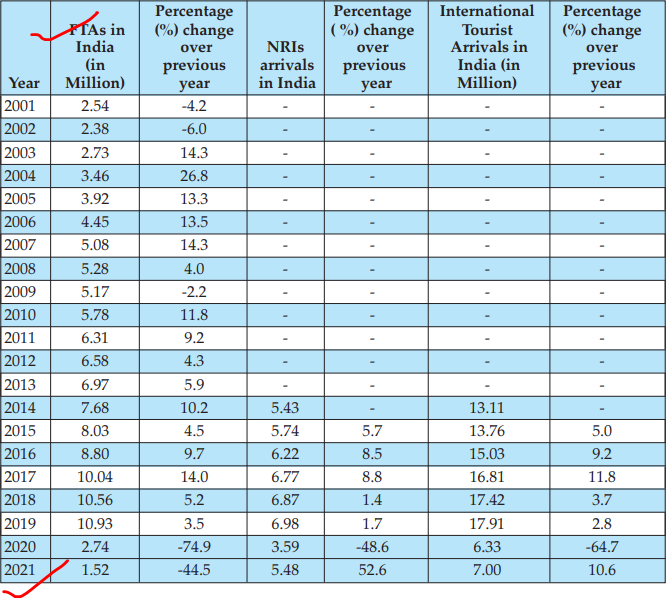











Current Affair 2:
Global Innovation Index 2022 (GII)
The Global Innovation Index 2022 (GII), in its 15th edition this year, is published by World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).


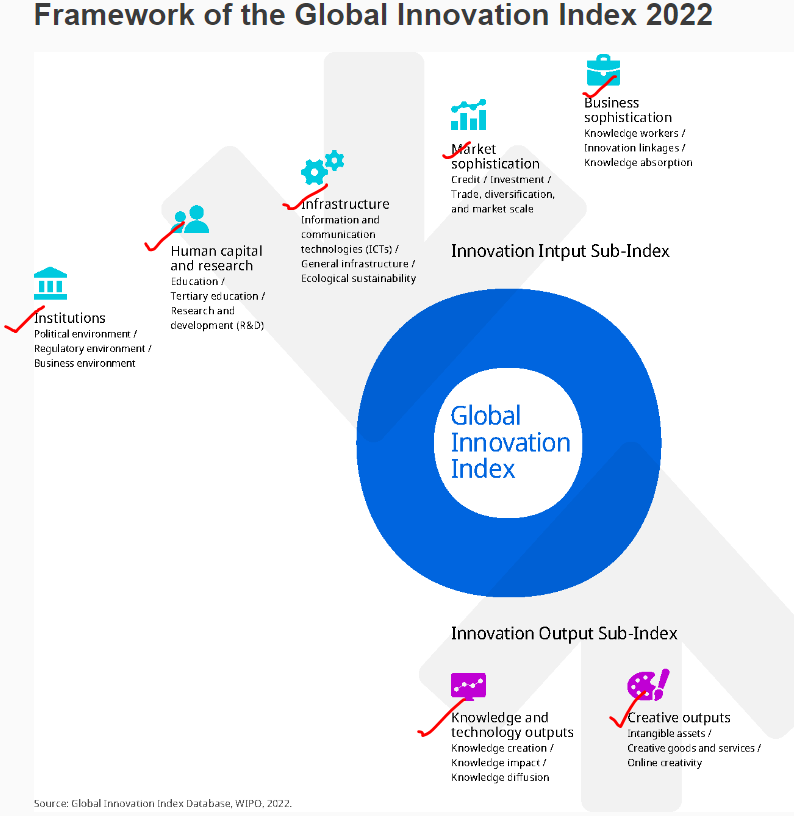


You don’t need anything more than this.
Current Affair 3:
How are tiger reserves notified in India?
The Uttar Pradesh (UP) cabinet September 27, 2022 approved the notification of the state’s fourth tiger reserve in the Ranipur Wildlife Sanctuary (RWS) in Chitrakoot district.
The Ranipur Tiger Reserve has tropical dry deciduous forests and is home to fauna such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, spotted deer, sambhar, chinkara and a number of birds and reptiles, the statement added.
The Ranipur Tiger Reserve will be the fourth in UP, after Dudhwa, Pilibhit and Amangarh (buffer of Corbett Tiger Reserve). It will also be the first in the state’s portion of the Bundelkhand region, which it shares with neighbouring Madhya Pradesh.
How are tiger reserves notified?
Tiger Reserves are notified by State Governments as per provisions of Section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 on advice of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.

The following steps are involved in the notification:
(a) Proposal is obtained from the State.
(b) In-principal approval is communicated from the National Tiger Conservation Authority, soliciting detailed proposals under section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
(c) National Tiger Conservation Authority recommends the proposal to the State after due diligence.
(d) The State Government notifies the area as a Tiger Reserve.
Current Affair 4:
Russia annexes 4 regions in Ukraine
Russian President Vladimir Putin presided over a ceremony to formally annex four Ukrainian regions. Key facts Eight years following the Russian annexation of Crimea, Moscow has captured four more Ukrainian territories – Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia and Kherson regions.
Just learn the map.

Current Affair 5:
What is glacial lake outburst flooding and how does it affect the Himalayas?
GLOF is the term scientists use to describe the incident when the water levels of glacial lakes breach their boundaries, causing large amounts of water to flow into nearby streams and rivers. These also create flash floods. Experts attribute GLOFs to climate change and the increase of anthropogenic footprints on glaciers.
A glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) is a release of meltwater from a moraine- or ice-dam glacial lake due to dam failure.

GLOFs have three main features:
- They involve sudden (and sometimes cyclic) releases of water.
- They tend to be rapid events, lasting hours to days.
- They result in large downstream river discharges (which often increase by an order of magnitude).
Why are glaciers in the Himalayas shrinking?
There are 2,000 glacial lakes in the Himalayas of which over 200 are vulnerable to outbursts.
According to scientists:
There are varied reasons for the increase of GLOF threats in the Himalayas.
- Glaciers in the Himalayas are shrinking very fast at the rate of 20 metre per year due to global warming.
- This increases the threat of a GLOF. Some glaciers may vanish in a few decades. In Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, most water requirements are met by glaciers.
- Glaciers are retreating due to climate change and increase in the anthropogenic footprint in the glaciers.
How does a GLOF impact the surrounding areas?
There are normal glaciers which are also called land terminating glaciers and they just release water, but do not pose any threat as a GLOF. But there are some glaciers which have a frontal region and also a bowl-shaped depression with accumulated water. When the volume of water in the lake increases; the confining moraine wall (accumulation of debris or material left by a moving glacier), is unable to contain the huge body of water and bursts, thus resulting in sudden release of water.
<< Previous Next >>



