Goaltide Daily Current Affairs 2023
Current Affair 1:
agriculture exports
The agriculture sector in India has experienced buoyant growth in the past two years.India’s agricultural exports are poised to scale a new peak in the financial year ending March 31, 2023. But
 |
so are imports, bringing down the overall farm trade surplus.
What are the opportunities to India’s Agriculture Exports?
India’s large extent of arable land, complemented by diverse agro-ecological conditions provide huge potential for cultivation of agriculture products.India’s spices and fruits are famous around the world for their high quality. India leads global production in several commodities. According to the FAO, India is the largest producer of milk, pulses and jute, and ranks as the second largest producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, groundnut, vegetables, fruit and cotton. India is also one of the leading producers of spices, fish, poultry, livestock and plantation crops.
Globally, India ranks second in total agricultural production at US$ 367 billion, yet India’s share in export market is minuscule. This indicates huge opportunity in scaling up the exports. As global value chain diversification becomes a priority around the world, India has an excellent opportunity to scale up agri-exports and rapidly transform the agri-economy.
Effective action at multiple levels, from farm inputs, quality assurance, traceability and certification, to building connections to global value chains (GVCs) can help India reach the US$ 100 billion milestone in agri-food exports in the next few years.
What are the benefits of enhancing India’s Agriculture Exports?
Largest sources of livelihood: Agriculture, with its allied sectors, is the largest source of livelihoods in India. It employs 152 million Indians as of 2021. 70% of rural households still depend primarily on agriculture for their livelihood.
Increase Farmers Income: Increase in export of agri-commodities at globally competitive prices will help increase income for farmers. However, there is a need to ensure that farmers, instead of middlemen, benefit from the farm exports.
Rural Development: Improvement in farm incomes will boost rural demand and contribute to growth of rural economy and development.
Trade Balance: Agriculture exports have consistently outperformed agri-imports. Agriculture sector has regularly maintained a trade surplus. This helps in mitigating Current Account Deficit (CAD) and help enhance forex reserves.
What are the challenges to India’s Agriculture Exports?
Inward-looking policies: India’s agriculture policy is focused more on food security and price stabilization, impacting policy approach to agriculture exports. This was evident recently with bans on exports of wheat and rice. Agri-exporters are impacted by frequent flip-flops in the policy. The policy deprives farmers of higher prices in the international market. Import restrictions when international prices are at a peak, reduce incentives for farmers to cultivate exportable crops.
Value Addition: Majority of India’s agriculture exports consist of low-value and semi-processed items which have limited demand in global markets. The proportion of food processed in India (of the total production) is very low.
Lack of uniformity: Lack of uniform quality standards, standardization of commodities and high losses in value chain have limited the potential of export of horticulture produce.
Maximum Residue Limit (MRL): India’s agricultural products are rejected to presence of Pesticide and chemical residues above the Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) of importing nations. In the past, India’s products like basmati rice, grapes and peanuts have been rejected.
The lack of awareness among farmers regarding the appropriate amount and timely use of chemicals is a major obstacle.
agriculture exports
The agriculture sector in India has experienced buoyant growth in the past two years.India’s agricultural exports are poised to scale a new peak in the financial year ending March 31, 2023. But
 |
so are imports, bringing down the overall farm trade surplus.
What are the opportunities to India’s Agriculture Exports?
India’s large extent of arable land, complemented by diverse agro-ecological conditions provide huge potential for cultivation of agriculture products.India’s spices and fruits are famous around the world for their high quality. India leads global production in several commodities. According to the FAO, India is the largest producer of milk, pulses and jute, and ranks as the second largest producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, groundnut, vegetables, fruit and cotton. India is also one of the leading producers of spices, fish, poultry, livestock and plantation crops.
Globally, India ranks second in total agricultural production at US$ 367 billion, yet India’s share in export market is minuscule. This indicates huge opportunity in scaling up the exports. As global value chain diversification becomes a priority around the world, India has an excellent opportunity to scale up agri-exports and rapidly transform the agri-economy.
Effective action at multiple levels, from farm inputs, quality assurance, traceability and certification, to building connections to global value chains (GVCs) can help India reach the US$ 100 billion milestone in agri-food exports in the next few years.
What are the benefits of enhancing India’s Agriculture Exports?
Largest sources of livelihood: Agriculture, with its allied sectors, is the largest source of livelihoods in India. It employs 152 million Indians as of 2021. 70% of rural households still depend primarily on agriculture for their livelihood.
Increase Farmers Income: Increase in export of agri-commodities at globally competitive prices will help increase income for farmers. However, there is a need to ensure that farmers, instead of middlemen, benefit from the farm exports.
Rural Development: Improvement in farm incomes will boost rural demand and contribute to growth of rural economy and development.
Trade Balance: Agriculture exports have consistently outperformed agri-imports. Agriculture sector has regularly maintained a trade surplus. This helps in mitigating Current Account Deficit (CAD) and help enhance forex reserves.
What are the challenges to India’s Agriculture Exports?
Inward-looking policies: India’s agriculture policy is focused more on food security and price stabilization, impacting policy approach to agriculture exports. This was evident recently with bans on exports of wheat and rice. Agri-exporters are impacted by frequent flip-flops in the policy. The policy deprives farmers of higher prices in the international market. Import restrictions when international prices are at a peak, reduce incentives for farmers to cultivate exportable crops.
Value Addition: Majority of India’s agriculture exports consist of low-value and semi-processed items which have limited demand in global markets. The proportion of food processed in India (of the total production) is very low.
Lack of uniformity: Lack of uniform quality standards, standardization of commodities and high losses in value chain have limited the potential of export of horticulture produce.
Maximum Residue Limit (MRL): India’s agricultural products are rejected to presence of Pesticide and chemical residues above the Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) of importing nations. In the past, India’s products like basmati rice, grapes and peanuts have been rejected.
The lack of awareness among farmers regarding the appropriate amount and timely use of chemicals is a major obstacle.
Current Affair 2:
Micro Led
Apple is reportedly working on a new display technology called microLEDs, which is considered the next big thing in the display industry.MicroLEDs are self-illuminating diodes that have brighter and better colour reproduction than Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display technology.
What are MicroLEDs ?
About:
MicroLED technology is based on the use of sapphires, which are known for their ability to shine on their own indefinitely.
The technology involves the use of tiny light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that are packed tightly together to create a bright and high-quality display.Unlike OLED displays, microLED displays use inorganic material such as gallium nitride.
A microLED is as small as cutting a centimetre of hair into 200 smaller pieces. Each of these microLEDs are semiconductors that receive electric signals.Once these microLEDs are gathered, they form a module. Several modules are then combined to form screens.
Benefits
MicroLED displays are brighter, have better colour reproduction and provide better viewing angles.
MicroLEDs have limitless scalability, as they are resolution-free, bezel-free, ratio-free, and even size-free.The screen can be freely resized in any form for practical usage.
Working Principle
The micro LED uses Indium Gallium Nitride semiconductors. In micro LEDs, each pixel can be turned ON or turned OFF. This cannot be done with conventional LEDs. Therefore, you get perfect colour control and contrast with micro-LED displays. The life of micro LEDs is longer. They can emit light continuously for more than 100,000 hours. That is, non-stop use for 11 years!
 |
Why are micro LEDs better?
The LCD displays in the market today use LED as backing light and a liquid crystal layer to create the image. The image is created by blocking the light on the crystal wherever required. There are no such complications with micro LEDs. Each and every LED on the screen can be controlled. Therefore, the image resolution is high, response time is less and power consumption is less.
Current Affair 3:
H5N1 Avian Influenza?
Recent reports of H5N1 (subtype of avian influenza) being transmitted between mammals have raised concerns about its potential to cause a human pandemic.
Scientists are investigating a potential spillover event after a mass mortality event that killed over 700 seals along the Caspian Sea coast where a H5N1 variant was detected in wild birds a few months ago.
What is H5N1 Avian Influenza?
About:
Avian influenza or bird flu refers to the disease caused by infection with avian influenza Type A viruses.
Infrequently, the virus can infect mammals from birds, a phenomenon called spillover, and rarely can spread between mammals.
H5N1, a subtype of avian influenza, has the potential to infect other mammals such as minks, ferrets, seals, domestic cats, and others through contact with infected birds, their faeces, or infected bird carcasses.
 |
Modes of Transmission of Avian Influenza
Direct contact between infected and healthy birds is how avian influenza primarily spread. It is found in secretions from nostrils, mouth eyes etc. HPAI infection is spread through people from infected poultry, the disease itself is not airborne.
Although it is possible for humans to contract the avian influenza virus from birds, human-to-human contact is much more difficult without prolonged contact.
The following man made ecosystems have contributed to the spread of avian influenza:
Indoor commercial poultry
Range-raised commercial poultry
Live poultry markets
Hobby flocks
Bird collection and trading systems
Out of the 5, it’s indoor commercial poultry that has the largest impact when it comes to the spread of Avian influenza. The rate of spread has only increased in the 1990s.
Impact of Avian Influenza
World Health Organization member states have recognised the need for a transparent system regarding sharing of vaccines and benefits from other networks. Cooperative measures created inresponse to HPAI have served as a basis for programs related to other emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases.
About 20% of the protein consumed is from the poultry industry. Periodic infections from bird flu does have an impact on poultry consumption as infected birds are culled in large numbers. In Vietnam alone, 50 million birds were culled as part of infection control programs. As per a report by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) economic losses in South East Asia totalled around US$ 10 billion.
The impact on small commercial farmers is the greatest. Government compensation for the lost poultry has varied from time to time. Some received compensation far below the market rate, while some received no compensation at all.
Poultry is one of the cheapest sources of proteins available. The loss of poultry birds will mean loss of food security for low-income groups. Now, as of 2021, there have been certain strains which have been infecting humans of late. Due to the close contact nature of the poultry industry, it is likely that there is another pandemic in the making.
Current Affair 4:
Meteorite
Scientists from Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, are claiming that the meteorite that crashed in two villages in Banaskantha, Gujarat on August 17, 2022, has been identified as an aubrite.The PRL group used a gamma-ray spectrometer to determine the mineral composition of aubrite. The group also classified the meteorite as a monomict breccia.
What are the Major Highlights Related to Aubrite?
Aubrite meteorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock that formed in oxygen-poor conditions and contains exotic minerals not found on Earth.For example, the mineral heideite was first described in the Basti meteorite.India has seen hundreds of meteorite crashes, but this is only the second recorded crash of an aubrite. The meteorite has been named the Diyodar meteorite after the taluka in which the villages are located.
The last crash of an aubrite before this was in Basti, Uttar Pradesh on December 2, 1852.
Around 90% of the meteorite was composed of orthopyroxene. Pyroxenes are silicates consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra (SiO 4); orthopyroxenes are pyroxenes with a certain structure. Pyroxenes such as diopside and jadeite have been used as gems. Spodumene was historically used as lithium ore. Rocks with pyroxene have also been used to make crushed stone that is used in construction. Aubrites have crashed in at least 12 locations worldwide since 1836, including 3 in Africa and 6 in the U.S.
Meteorite:
A meteorite is a term given to a piece of a comet or asteroid that falls into the earth’s atmosphere and survives to hit the surface. These objects come in three easy-to-remember categories: stony, metallic and stony metallic.
 |
Significance of Studying meteorites:
Scientists are interested in studying meteorites as examining them offers clues about the beginning of the solar system and maybe even the Earth. Space agencies have launched specific missions to asteroids to be able to study them. One such example is NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission launched in 2018 with the aim of reaching asteroid Bennu and getting back a sample from the ancient asteroid.
 |
Current Affair 5:
black soldier Fly Larvae
India is among the top five chicken and egg producers in the world, but there are challenges to the business for small poultry farmers because of the quality, quantity and cost of feed.Black soldier fly, since it has a high nutritional value can be one of the substitutes to address these challenges.
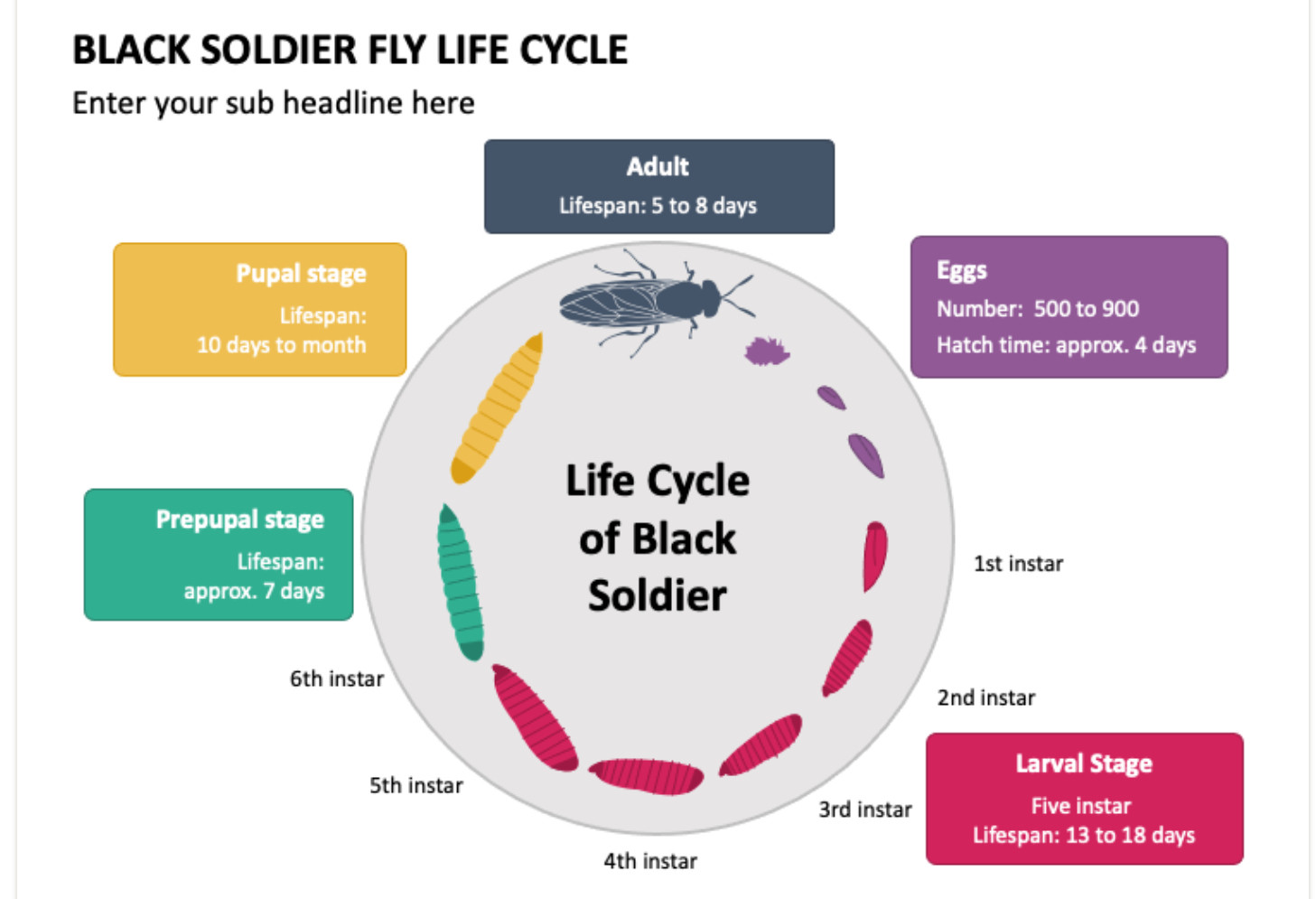 |
What are the Challenges Related to Poultry Feed?
Feeds account for up to 70% of the entire cost of poultry production. Besides, the conventional feed supplied to the poultry, majorly cereals and soya, competes with the food demands of a growing human population.In addition to rising cost, the feed resource availability is a major determinant of the sustainability of the poultry sector.One such alternative is brewers dried grains, a byproduct of the brewing industry.Though rich in protein and amino acid, its limitations include high moisture and fibre content.
Rice bran is another economically viable alternative to wheat in certain parts of the country. It has a comparable apparent metabolisable energy as wheat.However, studies show that the laying performance of the chicks declined on incorporation of rice bran to the feed.
The larvae of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens), for instance, have a high nutritional value and are easy to raise.
The trap consists of two major components, the primary collection vessel (PCV) and a larval segregation bucket (LSB), which together cater to the entire process of egg-laying, hatching and segregation of larvae. The gas release cum egg-laying assembly is placed at the top of the primary collection vessel and acts as the stimulator to facilitate movement of the fly.
 |
The egg-laying assembly is designed to make the system capable enough to effectively hold and hatch the eggs.A bottom composite drainage layer of 7-8 cm, comprising coconut coir and sand, is used to captivate larval movement towards the drain valve and primary screening of the leachate.The leachate is recirculated back into the system to withhold the moisture content between 50 and 60 per cent and also to ensure automated larval movement towards the segregation bucket
A full-grown larva older than a week consumes nearly 200 ml of diet every day. Therefore, the frequency of refilling the substrate (or waste products) in the reactor of the trapping mechanism is a direct variable of the larval count. With 9 gm of average larval weight and germination rate of 15,000 gm per day, the active count of larvae is up to 400 sq cm of substrate area.
At this consumption and germination rate, the substrate requires refilling every 18 days. Anyhow, during the experiment 15 days refilling frequency was practised to avoid the risk of starvation. Larval footprints have been recorded from the fifth day onwards and soon 2 kg of larvae were harvested per day over the next 20 days.
<< Previous Next >>


