Goaltide Daily Current Affairs 2023
Current Affair 1:
VOSTRO ACCOUNTS
20 Russian Banks have opened Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVA) with partner banks in India for the settlement of payments in rupee for trade between India and Russia. Also, all major domestic banks have listed their nodal officers to sort out issues faced by exporters under the arrangement.

A Vostro account is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency, in this case, the rupee. The SRVA is an additional arrangement to the existing system that uses freely convertible currencies and works as a complimentary system. All exports and imports must be denominated and invoiced in domestic currency (e.g. Rupee)
The exchange rate between the currencies of the trading partner countries would be market-determined
The final settlement also takes place in domestic currency (e.g. Rupee)
Banks include approval from the apex banking regulator (e.g. RBI)
The correspondent bank is not from a country mentioned in the updated FATF Public Statement on High Risk & Non-Co-operative jurisdictions All reporting of cross-border transactions is to be done in accordance with the extant guidelines under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999.
Advantages of Vostro and Nostro Accounts
They help in executing large foreign exchange transactions without having any physical presence in other countries.
They enable banks to keep funds in foreign currency without any exchange rate risk.
It is easy to operate since it is a mere transfer of funds from one account to another in the same bank.
Disadvantage
A lesser rate of interest as compared to savings or current account.
It is generally more expensive since it is a facility provided by the home bank to execute foreign exchange transactions smoothly.
Rigorous regulations and laws are imposed for the operation of these accounts.
RBIs Directions Related to Rupee Vostro and Nostro Accounts
As per the Regulation 7(1) of Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016, AD (Authorized Dealer) banks in India have been permitted to open Rupee Vostro Accounts.
Accordingly, for settlement of trade transactions with any country, AD bank in India may open Special Rupee Vostro Accounts of correspondent bank/s of the partner trading country.
AD Banks are commercial banks, state co-operative banks and urban co-operative banks that are authorized by the RBI under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (“FEMA”) to deal in foreign exchange transactions, be it current account or capital account.
Current Affair 2:
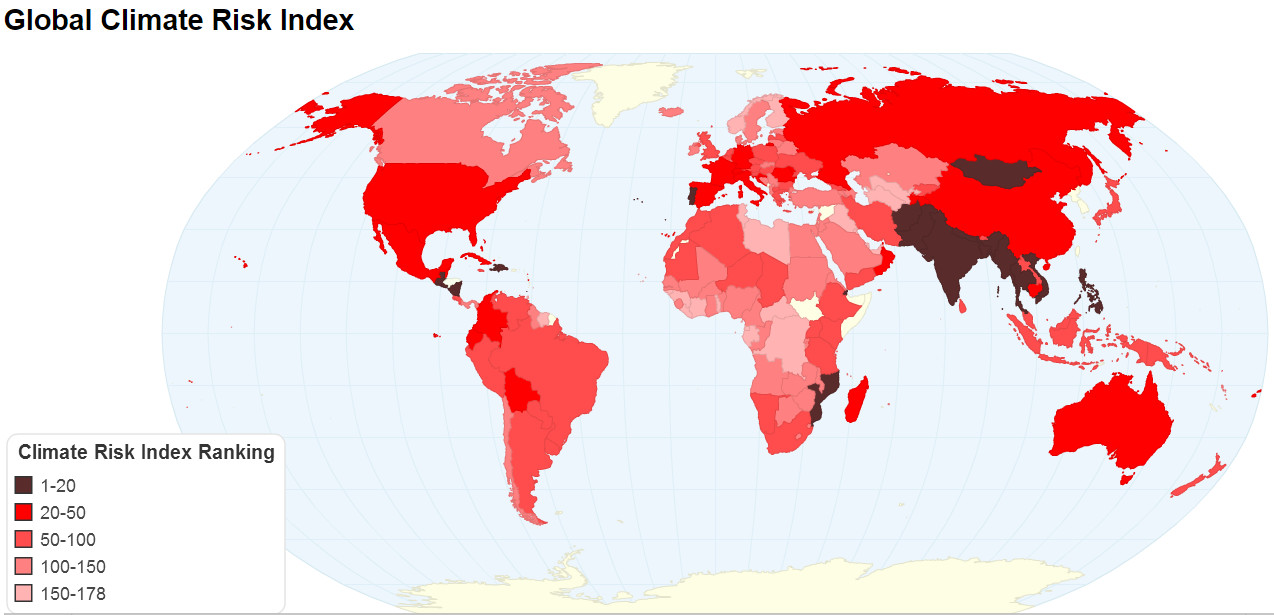
GROSS DOMESTIC CLIMATE RISK RANKING
According to Gross Domestic Climate Risk ranking by Cross Dependency Initiative (XDI), India has nine states in the 50 high risk states including Punjab, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Kerala and Assam.
Overall, India, China and the U.S. -- “globally significant states” -- are home to 80% of the most vulnerable cities and centres of economic activity around the world. Bihar (22nd spot), Uttar Pradesh (25th), Assam (28th), Rajasthan (32nd), Tamil Nadu (36th), Maharashtra (38th), Gujarat (48th), Punjab (50th) and Kerala (52nd) are among the most vulnerable in the country, with the index identifying the economic capital Mumbai to be at notable risk as well.
Two of China’s largest sub-national economies – Jiangsu and Shandong – top the global ranking. Asia dominates the list largely, with 114 of the top 200 regions falling in the continent. Physical risk Physical risk refers to vulnerability from eight climate change events: heat waves, coastal flooding (and sea level rise), extreme wind, forest fire, soil movement (or other drought-related hazards), free thaw, riverine and surface flooding.
Aggregated Damage Ratio (ADR) Together, the index assigned an Aggregated Damage Ratio (ADR) to each region, which signifies the total amount of damage a region’s built environment would sustain in 2050. A high ADR signifies more peril. According to the report, Assam, Bihar and Tamil Nadu had the highest ADR among other Indian States.
Assam, in particular, would witness the maximum increase of climate risk: rising up to 330% by 2050 as compared to 1990. Assam has experienced exponential increase in flood events since 2011, and it had 15 of India’s 25 districts most vulnerable to climate change.
Climate Fragility Risks in India
“A New Climate for Peace: Taking Action on Climate and Fragility Risks”, an independent report commissioned by members of the G7, identifies seven compound climate-fragility risks that pose serious threats to the stability of states and societies in the decades ahead:
Local resource competition: As the pressure on natural resources increases, competition can lead to instability and even violent conflict in the absence of effective dispute resolution.
Livelihood insecurity and migration: Climate changes will increase the human insecurity of people who depend on natural resources for their livelihoods, which could push them to migrate or turn to illegal sources of income.
Extreme weather events and disasters: Extreme weather events and disasters will exacerbate fragility challenges and can increase people’s vulnerability and grievances, especially in conflict-affected situations.
Volatile food prices and provision: Climate change is highly likely to disrupt food production in many regions, increasing prices and market volatility, and heightening the risk of protests, rioting, and civil conflict.
Transboundary water management: Transboundary waters are frequently a source of tension; as demand grows and climate impacts affect availability and quality, competition over water use will likely increase the pressure on existing governance structures.
Sea-level rise and coastal degradation: Rising sea levels will threaten the viability of low-lying areas even before they are submerged, leading to social disruption, displacement, and migration, while disagreements over maritime boundaries and ocean resources may increase.
Unintended effects of climate policies: As climate adaptation and mitigation policies are more broadly implemented, the risks of unintended negative effects—particularly in fragile contexts—will also increase
Current Affair 3:
INTERNATIONAL MOTHER LANGUAGE DAY
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) celebrates International Mother Language Day every year to promote mother tongue-based multilingual education. The theme for international mother language day: “Multilingual education – a necessity to transform education”, is aimed at emphasizing Indigenous people’s education and languages.
This has been kept into consideration based on the United Nations International Decade of Indigenous Languages (2022-2032) for which, UNESCO is the lead agency. It was Bangladesh’s initiative to introduce the idea of International Mother Language Day.
The day (February 21) also commemorates a long struggle by Bangladesh to protect its mother language Bangla. In November 1999, this day was proclaimed by the General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
The UN General Assembly welcomed the proclamation of the day in its resolution of 2002. On 16 May 2007 the United Nations General Assembly in its resolution called upon Member States “to promote the preservation and protection of all languages used by peoples of the world”.
The UNGA had then proclaimed 2008 as the International Year of Languages, to promote unity in diversity and international understanding, through multilingualism and multiculturalism.
 |
Importance of mother tongue:
Knowledge: Mother tongue provides a unique system of knowledge and understanding of the world. Mother tongue is the treasure we have inherited. It is the repository of our collective knowledge and wisdom which we have amassed over the course of the long journey of our vibrant civilization.
Peace: Promotion to mother tongue will enable sustainable development by enhancing investment, peace building and reconciliation among all the sections of society.
Rights: It is a fundamental human right and freedom of expression for indigenous people. Promotion to mother tongue will strengthen democratic principles.
Inclusion: It will help in social inclusiveness, improving literacy rates, reduction in poverty and international cooperation. Language can become catalyst for inclusive development. Removal of the existing linguistic barriers will help in realizing the goal of inclusive governance.
Diversity: Mother tongue shows our rich cultural values, diversity and heritage. We must accord a sense of dignity and pride to those who speak, write and communicate in these languages.
Mother tongue is the first language that a person learned. It is generally accepted that in teaching and learning processes, the child’s mother tongue is of utmost importance. For one thing, it categorizes a large part of the child’s environment, that is, it has names for most of the objects, actions, ideas, attributes and so on that are so important to him. Thus it will enhance formative learning.
It further promotes learning as the child feels more comfortable to express himself in a language he/she understands and can identify with. The knowledge so learned can be instantly applied in real world by the children as opposed to other language which they cannot instantly relate to.
Mother tongue helps in preservation of culture. India has rich culture of values, linguistic diversity and religious beliefs which can be protected and preserved through promotion to mother tongue.
Constitutional provision for indigenous languages:
Article 350 “Language to be used in representations for redress of grievances”: Every aggrieved person has the right to submit a representation for the redress of any grievance to any officer or authority of the Union or a state in any of the languages used in the Union or in the state, as the case may be. This means that a representation cannot be rejected on the ground that it is not in the official language.
Article 350A “Facilities for instruction in mother-tongue at primary stage”: Every state and a local authority in the state should provide adequate facilities for instruction in the mother-tongue at the primary stage of education to children belonging to linguistic minority groups. The president can issue necessary directions for this purpose.
Article 350B “Special Officer for linguistic minorities”: The president should appoint a special officer for linguistic minorities to investigate all matters relating to the constitutional safeguards for linguistic minorities and to report to him. The president should place all such reports before the Parliament and send to the state government concerned.
Current Affair 4:
AIR SERVICES AGREEMENT
The Union Cabinet chaired by Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently approved the signing of the Air Services Agreement between the Government of India and the Government of Co-operative Republic of Guyana.
The approval of the new Air Service Agreement (ASA) between India and Guyana will provide an enabling environment for enhanced and seamless connectivity while providing commercial opportunities to the carriers of both countries.
Indians have a sizable presence in Guyana and are the largest ethnic group comprising about 40% of the population. The ASA provides the legal framework for air operations between the countries which is based on the principles of sovereignty of nations, nationality of carriers and reciprocity in terms of commercial opportunities for designated airlines of each sides.
This agreement will enter into force after the exchange of diplomatic notes between the
 |
countries confirming that each party has completed the necessary internal procedure.
Guyana:
 |
Guyana is officially known as the Cooperative Republic of Guyana.
The country is bordered by;
The Atlantic Ocean in the North.
Brazil in the South and Southwest.
Venezuela in the West.
Suriname in the East.
it is one of the least densely populated countries on Earth.
It has a wide variety of natural habitats and very high biodiversity. It has one of the highest levels of biodiversity in the world.
Nearly 41% of the population lives below the poverty line.
The country’s population is racially and ethnically heterogeneous, with ethnic groups originating from India, Africa, Europe and China, as well as indigenous or aboriginal peoples.
It is the only South American nation in which English is the official language.
The main economic activities are agriculture, bauxite and gold mining, timber, shrimp fishing and minerals.
The economy has been transformed by the discovery of crude oil in 2015 and commercial drilling in 2019.
Current Affair 5:
EL NINO-LA NINAAb Nino-La Ni
India is experiencing a colder than normal winter thanks to the north-south winter flow set up by the climate phenomenon known as La Nina. The La Nina itself is going on for a record-breaking third consecutive year. Now, forecasts for the 2023 fall and winter are predicting that there is a 50% possibility for its companion phenomenon, the El Nino to occur.
El Nino
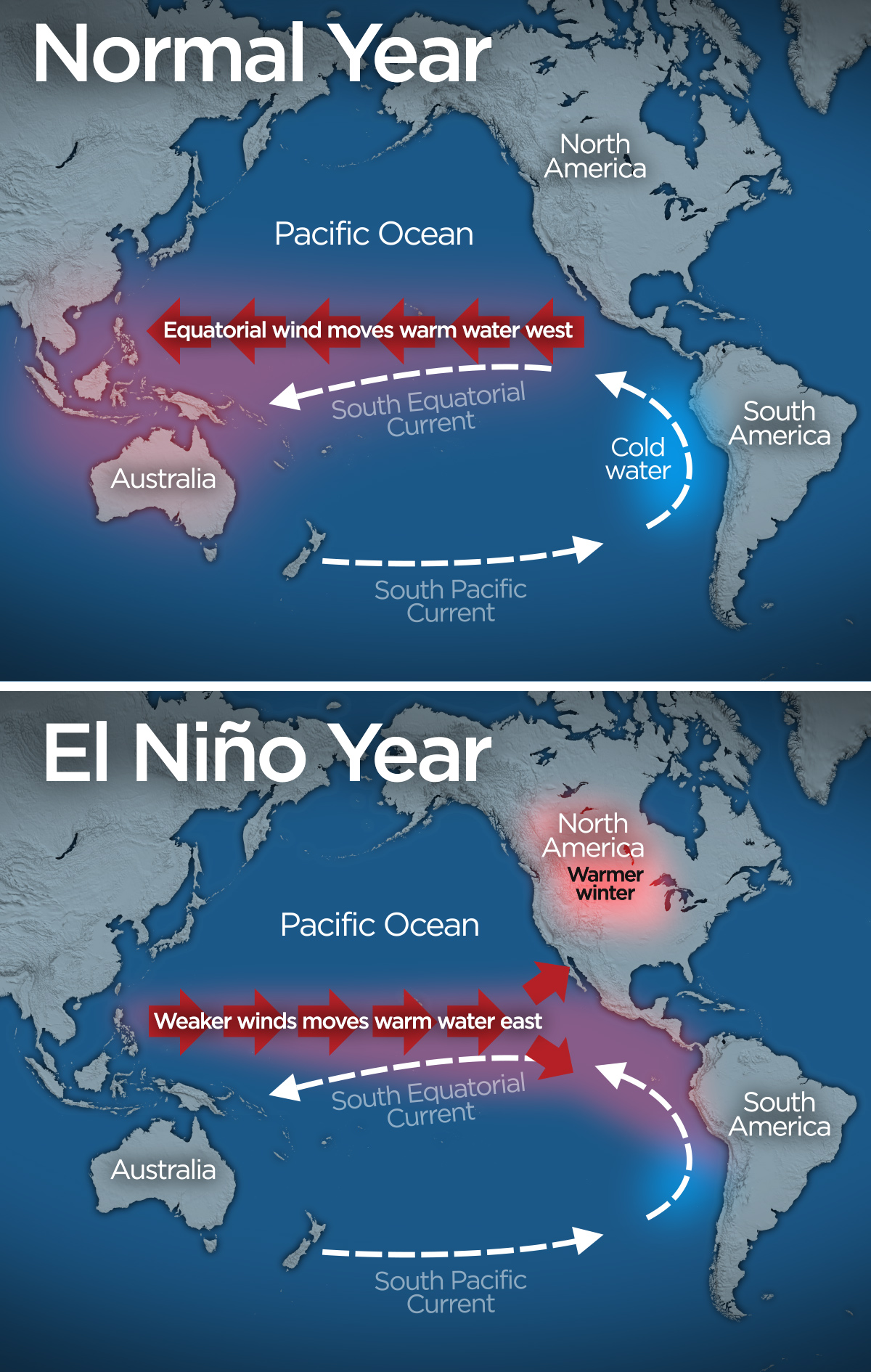
El Nino means ‘little boy’ or ‘Christ child’ in Spanish. The phenomenon was thus named because it was first recognised by South American fishermen in the early part of the 17th century. The events, i.e., warm waters in the Pacific Ocean, tended to occur in December, hence, the name was chosen.
El Nino refers to the large-scale ocean-atmosphere climate interaction linked to periodic warming in sea surface temperatures across the central and east-central Equatorial Pacific. It is associated with high pressure in the western Pacific. El Nino adversely impacts the Indian monsoons and hence, agriculture in India.
La nina
La Nina, the “cool phase” of ENSO, is a pattern that describes the unusual cooling of the tropical eastern Pacific. La Nina events may last between one and three years, unlike El Nino, which usually lasts no more than a year. Both phenomena tend to peak during the Northern Hemisphere winter.
La Nina means The Little Girl in Spanish. It is also sometimes called El Viejo, anti-El Nino, or simply "a cold event."
La Nina events represent periods of below-average sea surface temperatures across the east-central Equatorial Pacific.
It is indicated by sea-surface temperature decreased by more than 0.9℉ for at least five successive three-month seasons. La Nina event is observed when the water temperature in the Eastern Pacific gets comparatively colder than normal, as a consequence of which, there is a strong high pressure over the eastern equatorial Pacific.
In the ‘La Nina year’, rainfall associated with the summer monsoon in Southeast Asia tends to be greater than normal, especially in northwest India and Bangladesh.
This generally benefits the Indian economy, which depends on the monsoon for agriculture and industry.
Effect of El Niño
Convection over warmer surface water increases the likelihood of precipitation. South American rainfall has increased, causing erosion and coastal flooding.
Regions hit by tragedies caused by nature, such as flooding and drought, are more vulnerable to the spread of diseases.
Many areas contend that increased disease transmission is a result of El Nino flooding. Respiratory issues are brought on by cholera, dengue fever, malaria, and other illnesses.
Dryness is a result of El Nino in Australia and Indonesia. Water shortages result from reservoirs drying up and rivers not carrying enough water, endangering agricultural activity since we need water to irrigate land.
The El Nino influence has reduced the frequency of hurricanes in the Atlantic.
Effect of La Nina
It causes severe monsoons in Southeast Asia and India.
It causes a condition in Peru and Ecuador that resembles a drought.
It brings about chilly, wet winters in Southeast Africa and wet weather in Eastern Australia.
It causes winter draughts in the Southern United States.
It makes the winters in the northwest United States and western Canada extremely chilly.
In Australia, it leads to significant flooding.
The Western Pacific, the Indian Ocean, and the area off the coast of Somalia see high temperatures as a result.
It leads India to experience intense monsoon rains.
<< Previous Next >>


